What is a Modifier?
Modifiers are words or phrases that modify, describe, or add more details to another word in a sentence. Adverbs and adjectives are modifiers, so are phrases and clauses. Adverbs modify a verb, an adjective, or another adverb. Adjectives modify a noun or pronoun. Words may form phrases and clauses to modify another word.
- He arrived early. [the adverb early modifies the word verb]
- Your paintings are majestic. [the adjective majestic modifies the noun paintings.]
- The teacher from Spain gave us a language exam. [the phrase from Spain modifies the noun teacher.]
- My best friend who loves dogs adopted a puppy again. [the clause who loves dogs modifies the noun best friend.]
NOTE: Notice the change in the meaning of each sentence as we move about the modifying phrase from Spain.
- From Spain, the teacher gave us a language exam.
- The teacher gave us a language exam from Spain.
- The teacher from Spain gave us a language exam.
The first sentence means the teacher was in Spain when he or she gave the exam; the second, that the exam was from Spain; the third, that the teacher was from Spain. The placement of the modifying phrase from Spain changes the meaning of each sentence. Those are all clear and correct sentences, but you should aim for the one that says what you mean.
A seamless arrangement of words in a sentence is crucial for comprehension. So, make sure your words flow in a way that communicates what you mean.
Placement of Modifiers:
When modifiers are placed too far from the word they modify, common errors occur. To avoid confusion, place the modifying word or phrase near the word modified.
1. Prepositional Phrases as Modifiers
When using a prepositional phrase as a modifier, always place the phrase near the word it modifies.
NONSTANDARD: The bag was left on the bed with pink zipper. [With pink zipper should go with bag, not bed.]
STANDARD: The bag with pink zipper was left on the bed.
UNCLEAR: The woman was baking cookies in a red dress.
CLEAR: The woman in a red dress was baking cookies.
Related Reading: Prepositions: Answering When and Where
2. Participial Phrases as Modifiers
Participles are verbs that are used as adjectives. “The TV is broken” uses broken as a verb, while “The broken TV was sold” uses the verb broken as an adjective which makes it a participle. When this participle joins with other words, it becomes a participial phrase. “Broken by my sister, the TV was sold to a junkshop.”
When you use a participial phrase in the beginning of a sentence, make sure the word it modifies immediately follows the phrase. Otherwise, you’ll have a dangling modifier.
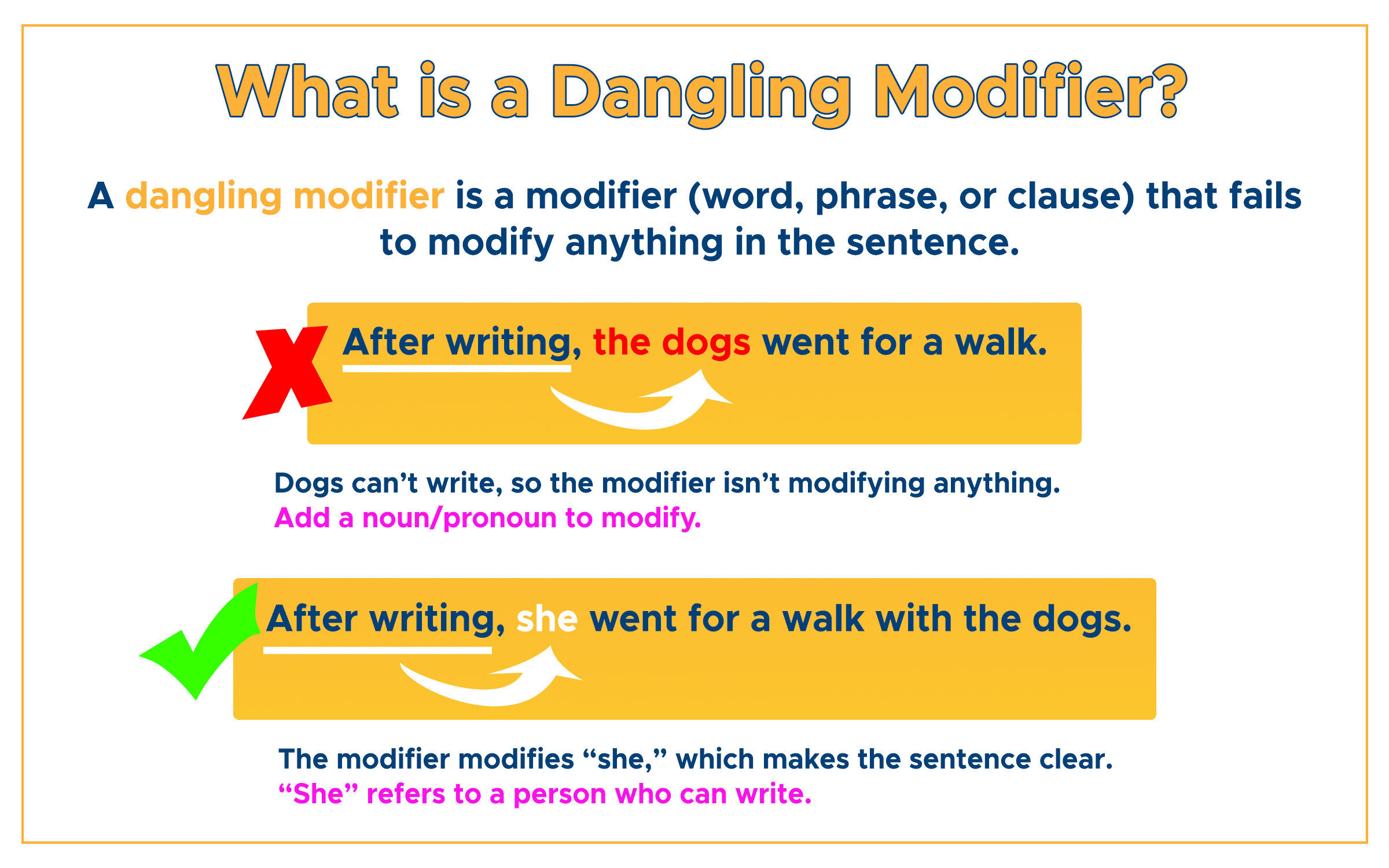
CORRECT: After doing a lot of interviews, she is finally done with her thesis. [The participial phrase after a doing a lot of interviews modifies the noun she, which immediately followed after the phrase.]
DANGLING: After doing a lot of interviews, the thesis is finally done.
The modifier after doing a lot of interviews is dangling because the noun being modified did not immediately follow. The noun thesis cannot possibly be the doer of the phrase, so supply a word that matches the modifier, just like in the correct example above.
DANGLING: Offended by his remarks, an apology is what she wants. [The dangling modifier is offended by his remarks because the noun apology was not offended, she was.]
CORRECTED: Offended by his remarks, she wants an apology. [Notice the omission of the word what to make the sentence short and clear.]
3. Clauses as Modifiers
Form clauses by joining adjectives and adverbs with other words. Make sure to place the clauses as near as possible to the words modified. Otherwise, you’ll have a misplaced modifier.
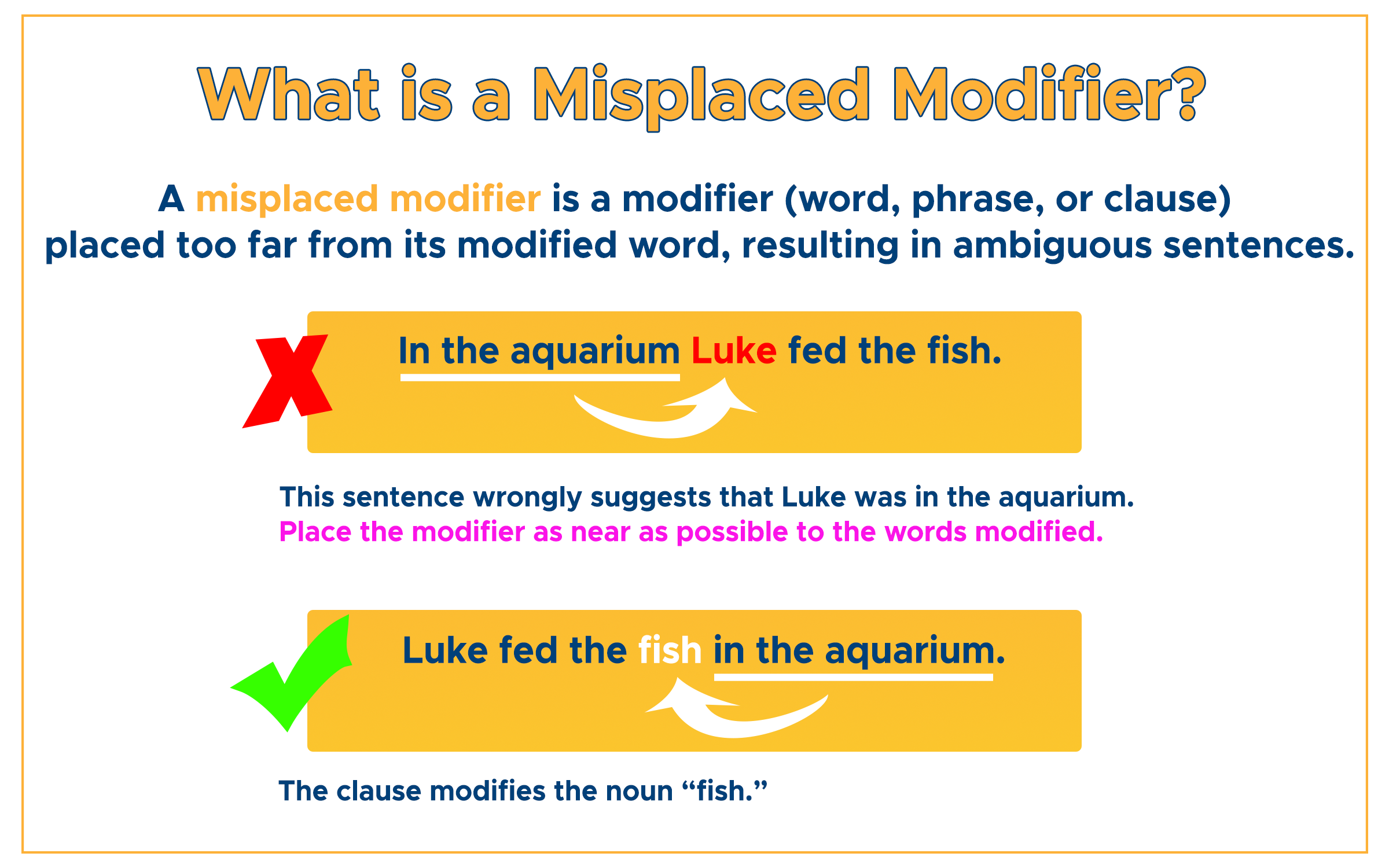
MISPLACED: The necklace was stolen in the market which she bought yesterday. [The sentence suggests that she bought the market.]
CORRECTED: The necklace which she bought yesterday was stolen in the market. [the clause modifies necklace]
MISPLACED: The movie was cancelled by its producer that was about the pandemic. [The movie was about the pandemic.]
CORRECTED: The movie that was about the pandemic was cancelled by its producer.
Practice:
Italicize the dangling or misplaced modifier/s in each sentence. Rewrite each sentence to correct the mistakes. Some of the sentences may have more than one correct version.
- In the mirror I saw a ghost at the restroom.
- Arriving late, the class was dismissed by the teacher.
- The flowers were delivered to the house which she ordered.
- Tired from work, I saw her sleeping on the couch.
- With a heart shape, Maddie saw a cloud.
Answers:
- In the mirror I saw a ghost at the restroom.
I saw a ghost in the mirror at the restroom.
At the rest room, I saw a guest in the mirror.
- Arriving late, the class was dismissed early by the teacher.
Arriving late, the teacher dismissed the class early.
- The flowers were delivered to the house which she ordered.
The flowers which she ordered were delivered to the house.
- Tired from work, I saw her sleeping on the couch.
Tired from work, she was sleeping on the couch.
- With a heart shape, Maddie saw a cloud while resting in the park.
Maddie saw a cloud with a heart shape while resting in the park.
While resting in the park, Maddie saw a cloud with a heart shape.
Thank you for reading. We hope it’s effective! Always feel free to revisit this page if you ever have any questions about sentence modifiers.

