Let’s learn how to determine the volume of a cube.
What is a Cube?
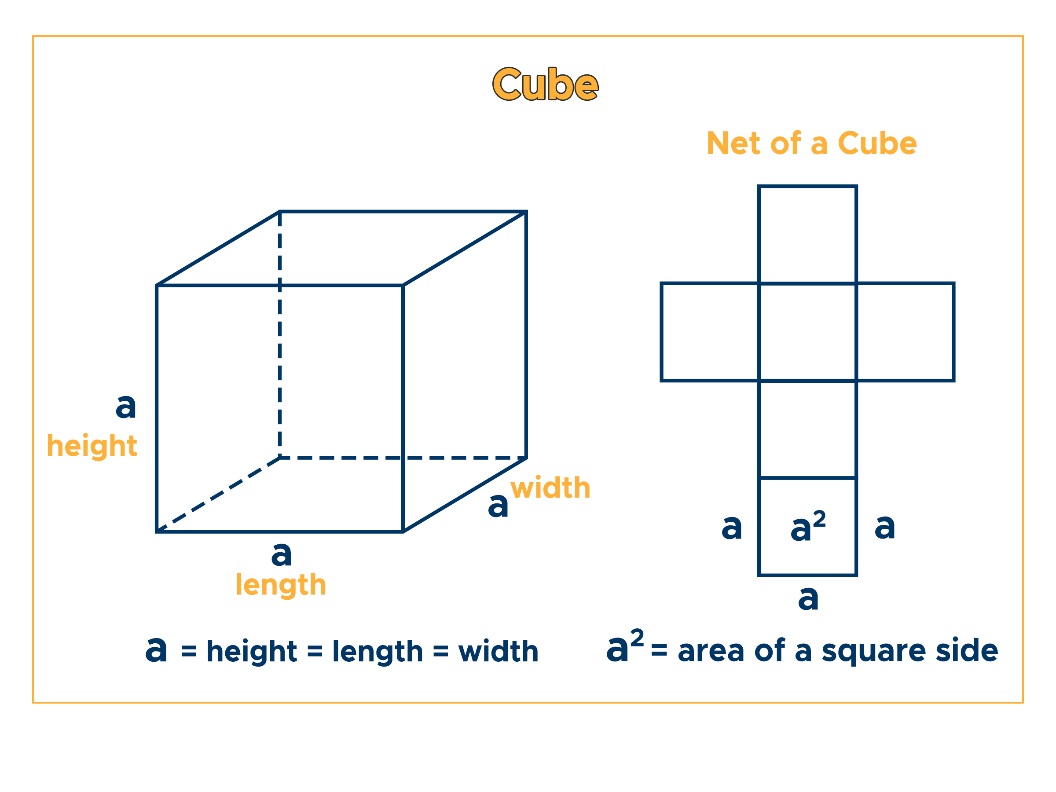
The only regular hexahedron, a cube is a three-dimensional object with six equal-sized square surfaces or sides, 12 edges, and 8 vertices. Given that its square sides are equal, it follows that a cube’s length, width, and height are equal, too. Examples of cube-shaped objects are dice, jewelry boxes, ice cubes, sugar cubes, and Rubik’s cubes.
Here’s an illustration of a cube. Notice how it forms 6 equal square surfaces or sides when unfolded. The resulting two-dimensional shape when a cube is unfolded is called the cube’s net.
How to Find the Volume of a Cube:
The volume of a cube not only tells the amount of space it occupies but also measures its capacity or the amount of space inside an object that can be filled. When you have a hollow cubic container you want to fill with water, the cubic container’s volume is needed to determine its capacity i.e. how much water it can hold.
Note: Volumes are measured in cubic units such as cm3, m3, km3, and in3. When referring to the cube’s capacity, volume can be measured in liter (L) or milliliter (mL).
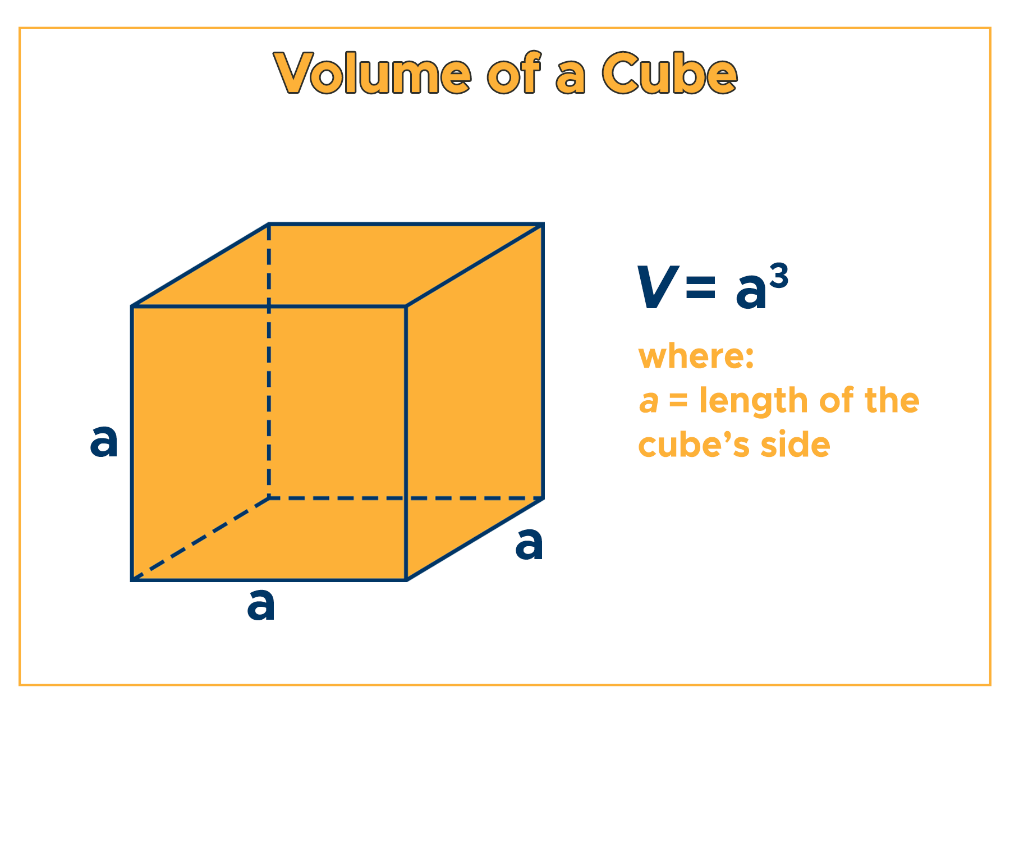
To find the volume of a cube, multiply its length by its width and height (a • a • a). Given that all lengths of a cube’s square sides are the same, its volume formula is written as:
V = a3
where a = length of the cube’s one side
Quick Guide to Finding the Volume of a Cube:
Step 1. Write the given figures. You’ll need the length of the cube’s side to find the volume. Make sure all measurement units are the same. If not, convert either of them to match the other.
Step 2. Plug the figures into the formula.
Step 3. Perform the operations. Don’t forget to write the cubic unit for volume.
Example #1: Find the Volume of a Cube when given the Length of One Side
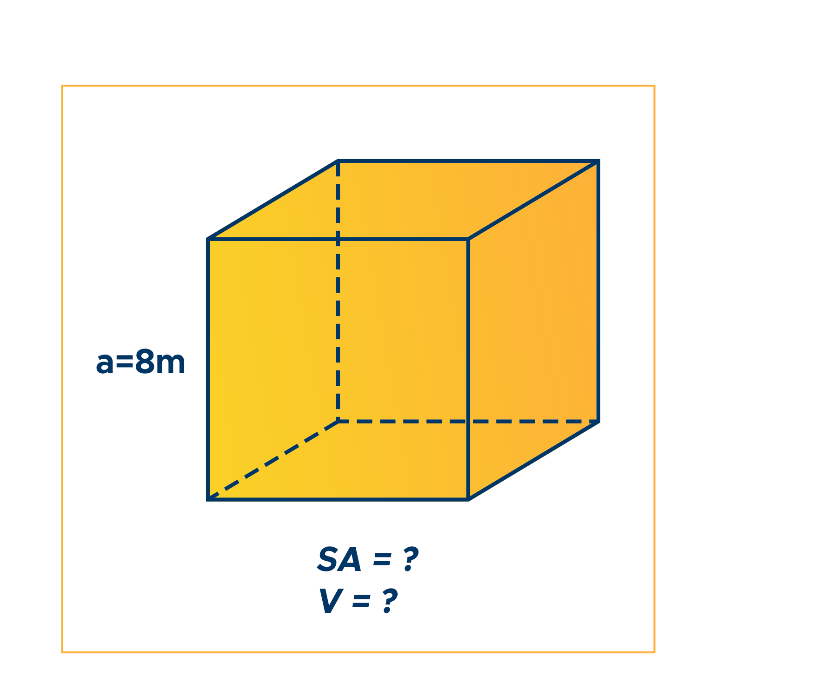
Find the volume of the cube below.
Solution for Example #1:
Step 1. Write down the given measurement, a = 8m.
Step 2. Plug 8m into the formula for volume of a cube.
V = a3
V =(8cm)3
Step 3. Simplify & solve the equation.
V = 512cm3
Therefore, the volume of the cube is 512cm3.
Want to learn how to find the surface area for this cube?
Related Reading: Surface Area of a Cube – Formula & Examples
Example #2: Find the Volume of a Cube when given the Length of One Side
Find the volume of a cube whose length is 3cm.
Solution for Example #2:
Step 1. Write down the given measurement, a = 3cm.
Step 2. Plug 3cm into the formula for volume of a cube.
V = a3
V =(3cm)3
Step 3. Simplify & solve the equation.
V = 27cm3
Therefore, the volume of the cube is 27cm3.
Example #3: Finding Length & Surface Area when given Volume
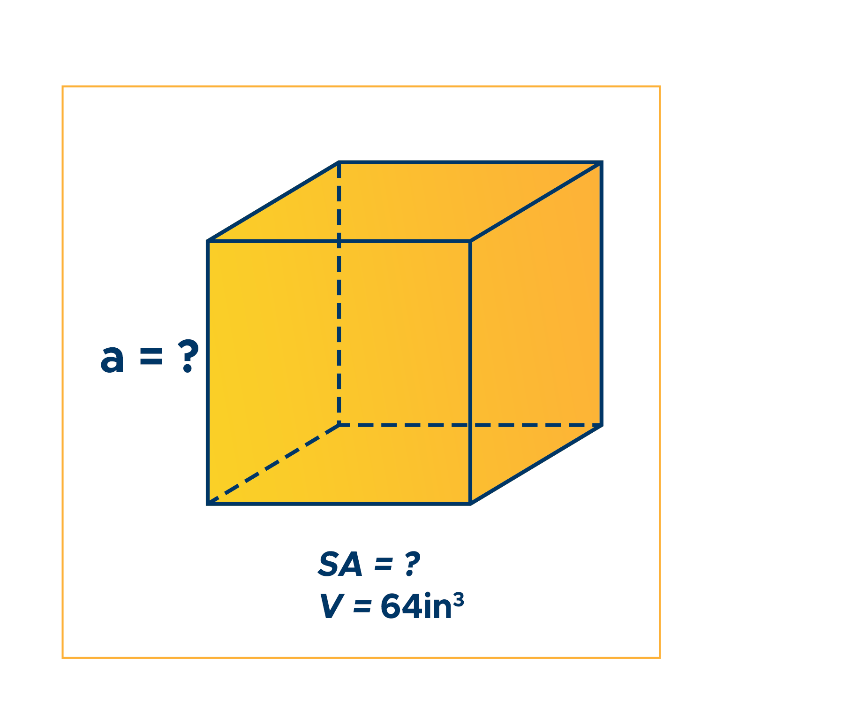
Find the length and surface area of the cube below.
Solution for Example #3:
Begin by finding the length of the cube (a).
Step 1. Write the given measurement, V = 64in3.
Step 2. Determine the length of the cube (a) by finding its volume’s cube root, given by the formula:
a = 3√V
Note: This formula is found by taking the cube root of both sides of the volume equation, V = a3.
Step 3. Substitute 64in3 for V in the formula, then simplify & solve the equation.
a = 3√(64in3)
a = 4in
Therefore, the length of the cube is 4in.
Now, we can find the surface area of the cube by using the length we found.
Step 1. Substitute 4in for a in the formula for a cube’s surface area.
SA = 6a²
SA = 6(4in)²
Step 2. Simplify & solve the equation.
SA = 6(4in)²
SA = 96in²
Therefore, the surface area of the cube is 96in².
Example #4: Determine the Capacity of a Container
How many cubical boxes of 2cm x 2cm x 2cm can be placed inside a cubical container whose edge measures 6cm?
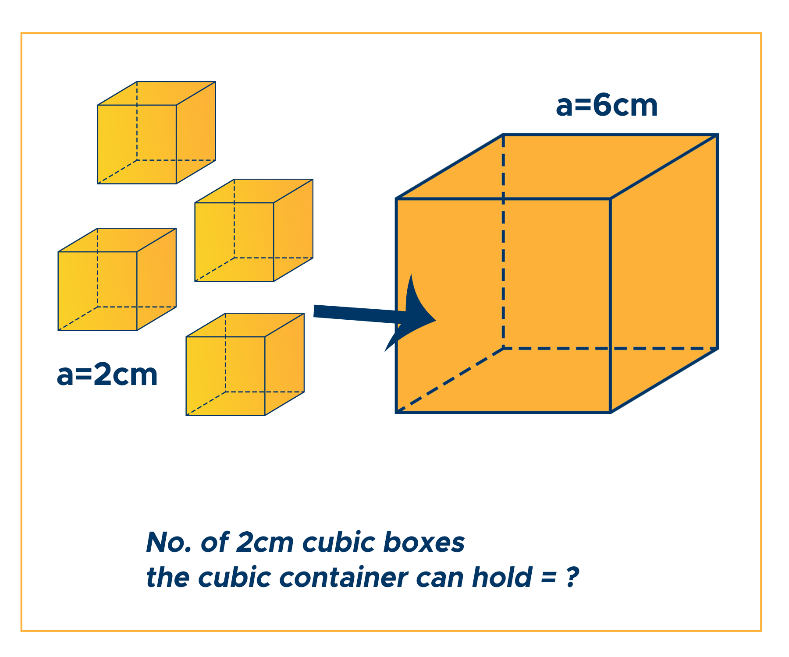
Solution for Example #4:
To find the number of boxes that can fit in the container, divide the container’s volume by the volume of the boxes.
Step 1. Write the given figures: length of cubical boxes (a = 2cm), length of cubical container (a = 6cm).
Step 2. Compute the volume of the cubical boxes first.
Substitute 2cm for a in the volume formula.
V = a3
V = (2cm)3
Simplify & solve the equation.
V = 8cm3
Therefore, the volume of each cubical box is 8cm3.
Step 3. Compute the volume of the cubical container.
Substitute 6cm for a in the volume formula.
V = a3
V = (6cm)3
Simplify & solve the equation.
V = 216cm3
Therefore, the volume of the cubical container is 216cm3.
Step 4. Divide the volume of the cubical container by the volume of each cubical box to find the number of boxes that will fit into the container.
Vcontainer / Vbox
216cm3 / 8cm3 = 27
Therefore, the cubical container with a 6cm length can hold 27 cubical boxes with 2cm length.
Thank you for reading. We hope it’s effective! Always feel free to revisit this page if you ever have any questions about the volume of a cube.
Check out some of our other blog posts or invest in your future with one of our self-study courses!



